Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is an important signal protein. Importantly, it is involved in angiogenesis and angiogenesis (blood vessels grow from a pre-existing vascular system). All members of VEGF family stimulate cell response by binding to tyrosine kinase receptors (VEGFRs) on the cell surface. Thus they dimerize and are activated by transphosphorylation. Particularly, VEGF-A regulates angiogenesis and vascular permeability by activating two receptors VEGFR-1 (Flt-1) and VEGFR-2 (KDR/Flk1 in mice). Obviously, VEGF-A has a variety of functions, including angiogenic activity, vascular permeability activity and stimulating cell migration in macrophage lineage and endothelial cells.
Specifically, VEGFR-2 is a major regulator of angiogenesis. VEGFR-2 is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK), which transduces biochemical signals through transverse dimerization in the plasma membrane. Interestingly, VEGF, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 are necessary for normal vascular development. VEGF is the main mediator of ocular neovascularization and it is relevant to retinal ischemia. Here, we will introduce a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, Axitinib.
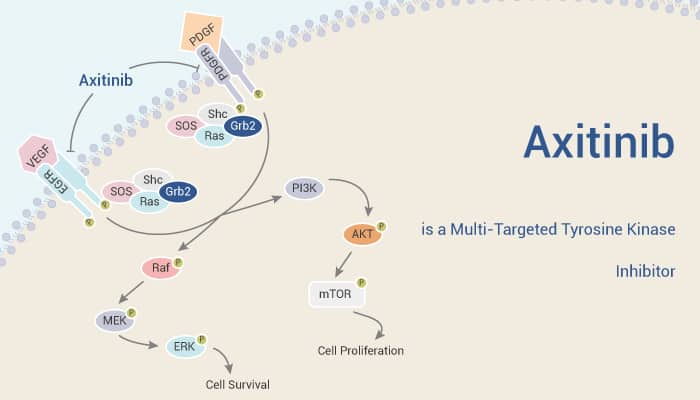
Axitinib is a Multi-Targeted Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor.
At first, Axitinib has IC50s of 0.1, 0.2, 0.1-0.3, 1.6 nM for VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3 and PDGFRβ, respectively. Besides, Axitinib effectively blocked growth factor-stimulated phosphorylation of VEGFR-2 and VEGFR-3 in transfected or endogenous RTK expressing cells. It has average IC50 values of 0.2 and 0.1 to 0.3 nm, respectively.
Secondly, Axitinib has about 8 to 25 times higher IC50 for closely related type III and V family RTKs. it includes PDGFR- β (1.6 nm), kit (1.7 nm), and PDGFR- α (5 nM). Moreover, Asitinib can prevent PDGF BB mediated human glioma U87MG cells migrating but does not prevent proliferation.
Thirdly, A single oral administration of Acitinib (100 mg/kg) significantly inhibited VEGFR-2 phosphorylation in mice for up to 7 hours. Furthermore, Axitinib dose-dependently inhibited VEGF-induced vascular permeability in mouse skin. Axitinib inhibits the growth of human xenograft tumors in mice.
All in all, Axitinib is a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
References:
Hu-Lowe DD, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 15;14(22):7272-83