c-Met (HGFR) is a membrane receptor that is essential for embryonic development and wound healing. Otherwise, HGF is the only known ligand of the c-Met receptor. Upon HGF stimulation, c-Met induces several biological responses that collectively give rise to a program known as invasive growth. Besides, HGF/c-Met signaling mediates a diverse biological activities, including proliferation, survival, motality, migration, branching morphogenesis, wound healing and angiogenesis. Therefore, c-Met has been targeted by several drug discovery programs.
As reported, Savolitinib (AZD-6094) is a highly selective and orally active inhibitor of the c-Met tyrosine kinase. Meanwhile, Savolitinib selectively binds to and inhibits the activation of c-Met in an ATP-competitive manner, and disrupts c-Met signal transduction pathways.In addition, Savolitinib shows potent anticancer effect in both preclinical and clinical studies, including NSCLC, breast, head and neck, colorectal, gastric, pancreatic, and other gastrointestinal cancers.
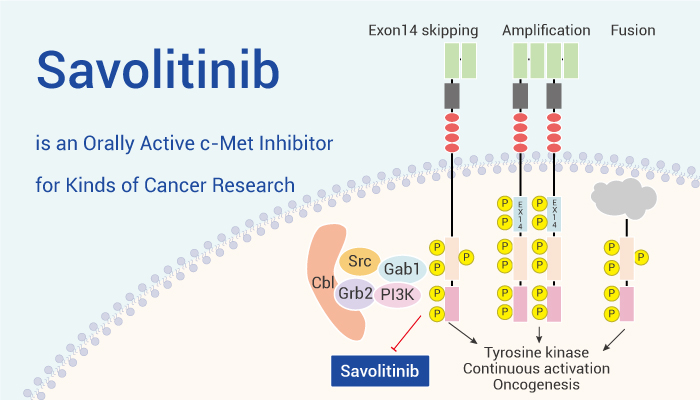
Savolitinib, a c-Met inhibitor, can be used for various cancer research.
In vitro, Savolitinib inhibits c-Met with IC50s of 5 nM and 3 nM for c-Met and p-Met, respectively. Moreover, Savolitinib shows >200‐fold selectivity against a diverse panel of kinases. Besides, Savolitinib shows anti‐proliferative activity against a panel of gastric tumor cell lines, with EC50s <100 nM. Furthermore, Savolitinib (100 nM, 1 h) inhibits phosphorylated forms of cMET, ERK1/2 and AKT in Hs746T cell lysates.
In vivo, Savolitinib (1-10.0 mg/kg; oral administration; daily; for 21 days; athymic nude mice) demonstrates dose-dependent tumor growth inhibition in a U87MG subcutaneous xenograft model. In addition, none of the mice in the dosing groups exhibits body weight loss during the experiment, indicating the antitumor effect and safety.
To sum up, Savolitinib is an orally active c-Met inhibitor. Savolitinib shows potent anticancer effects in various cells and animal models.
References:
[1] Jia H, et al. J Med Chem. 2014 Sep 25;57(18):7577-89.
[2] Lee TS, et al. Cancers (Basel). 2023 Sep 25;15(19):4708.
[3] Gavine PR, et al. Mol Oncol. 2015 Jan;9(1):323-33.