EGFR (epidermal growth factor receptor) is a transmembrane protein and is a member of the ErbB family. Besides, EGFR is a protein tyrosine kinase expressed on many types of tumor cells, including breast, ovarian, bladder, head and neck, and prostatic carcinoma. Mainly, In malignant tumors, EGFR overexpression is linked to poorer prognosis. Importantly, The activation of EGFR promotes angiogenesis, cell migration, survival, invasion and proliferation. So, It is important to find a potent EGFR inhibitor for cancer. In this article, we will introduce an anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody, Cetuximab (C225).
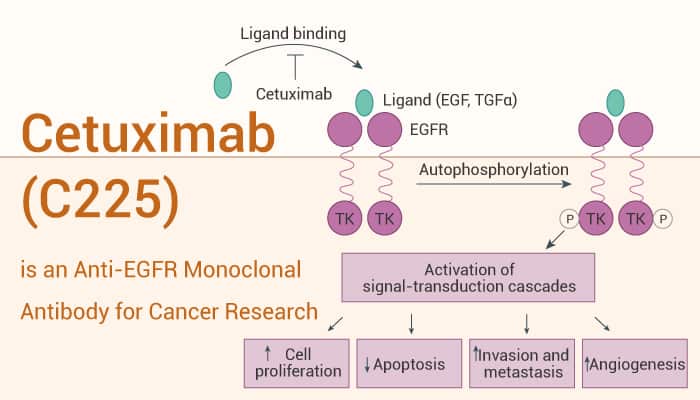
Cetuximab (C225) is an Anti-EGFR Monoclonal Antibody for Cancer Research
Cetuximab is a particular murine monoclonal antibody that binds specifically to the human EGFR with a Kd of 0.201 nM by SPR. Besides, It also exhibits a Kd of 0.147 nM for EGFR in fixed A431 cells by ELISA. In addition, Cetuximab (30 nM; 0-10 days) inhibits SCC-1, SCC-11B, SCC-38, and SCC-13Y cell proliferation in a time-dependent manner. Moreover, Cetuximab (30 nM; 2-4 days) induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 arrest in SCC-13Y cells. Meanwhile, Cetuximab (30 nM; 0-120 h) reduces Rb, p27KIP1, Bcl-2, and Bax expression in SCC-13Y cells. Additionally, Cetuximab (30 nM) also enhances radiosensitivity and increases radiation-induced apoptosis in SCC-13Y cells.
Cetuximab shows anti-tumor activity in vivo. For example, Cetuximab (1 mg; intraperitoneal injection; at day 10, 13, and 16 after injection of tumor cells) significantly inhibits tumor volume in UT-SCC-14 xenografts (BALB/c (nu/nu) female nude mice). Besides, In UT-SCC-14 xenografts, Cetuximab decreases the expression of EGFR, pEGFR, and Ki67 after 9 days of treatment. Moreover, in 6-8 weeks, female athymic nude mice (A431 cells; s.c.), Cetuximab (1 mg, 500 µg, 250 µg; i.p.; twice weekly for 5 weeks) significantly inhibits tumor growth in a dose-dependent manner.
All in all, Cetuximab is a human anti-EGFR monoclonal antibody. Besides, Cetuximab shows anti-tumor activity.
Reference:
[1] Goldstein NI, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 1995 Nov;1(11):1311-8.
[2] Gustafsson H, et al. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2017 Dec;75(3-4):299-309.
[3] Huang SM, et al. Cancer Res. 1999 Apr 15;59(8):1935-40.