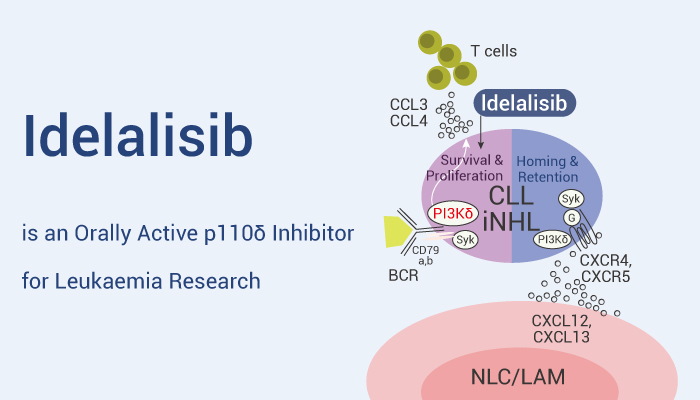
PI3K signaling is active in many B-cell leukemia and lymphomas. Moreover, the cell surface receptors (class I isoforms p110α, p110β, p110δ, and p110γ) mediates the activation of the PI3K pathway. Besides, p110δ is highly expressed in cells of hematopoietic origin, especially in leukocytes. Although PI3Kδ inhibitors (eg: Ibrutinib) are important strategies for the treatment of mature B cell malignancies, it’s still limited by toxicity, off-target activity and other problems. Therefore, Idelalisib (CAL-101), a highly selective and orally active p110δ, has great potential in hematologic malignancies. In addition, FDA has approved Idelalisib for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).
Idelalisib, a selective and orally active p110δ inhibitor, has anti-leukemia activity.
In vitro, Idelalisib shows high selectivity for p110δ relative to other PI3K class I enzymes (IC50: 2.5 nM, 820, 565, and 89 nM for p110δ, p110α, p110β, and p110γ respectively. In addition, Idelalisib (0-100 μΜ, 48 h) shows cytotoxicity in CD19+ cells from patients with CLL, as well as inducing caspase-dependent apoptosis (0-10 μΜ, 48 h). Besides, Idelalisib (0-100 μM, 48 h) has no cytotoxicity on normal T cells and NK cells. Simultaneously, Idelalisib inhibits constitutive PI3K signaling in lymphoma cells. Specifically, Idelalisib inhibits pAktS473, pAktT308, and the downstream target S6 with an EC50 of 0.1-1.0 μM in SU-DHL-5, KARPAS-422 and CCRF-SB cells.
In vivo, Idelalisib (30 mg/kg, oral gavage, daily) prolongs survival of heterotopic cardiac allografts in heterotopic cardiac transplant C57BL/6 mice model. Furthermore, the combination of Idelalisib (25 mg/kg, oral gavage, daily) and Ibrutinib (25 mg/kg, oral gavage, daily) inhibits tumor growth in Ibrutinib-resistant B-cell lymphoma-bearing PDX mouse models. The results indicates that Idelalisib can overcome the Ibrutinib resistance.
In conclusion, Idelalisib is a selective and orally active p110δ agonist, and can be used for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), B-cell leukemias and other cancers research.
References:
[1] Lannutti BJ, et al. Blood. 2011 Jan 13;117(2):591-4.
[2] Herman SE, et al. Blood. 2010 Sep 23;116(12):2078-88.
[3] Cooney JD, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Mar 1;24(5):1103-1113.
[4] Zhang L, et al. Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Aug 1;23(15):4212-4223.