Disulfiram (DSF) is a drug for the treatment of chronic alcoholism. It first received pharmacological attention in 1880, when it was used externally to treat itch. For the treatment of alcoholism, it was first used by Hald, Jacobsen, and Martensen-Larsen at Medicinalco, in 1948.
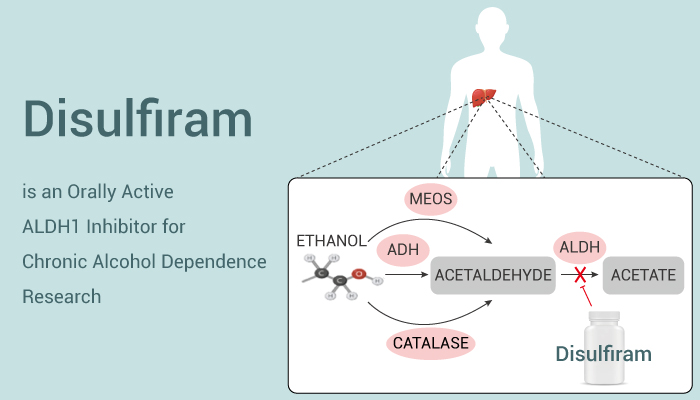
DSF is a well-known anti-alcohol agent that inhibits aldehyde dehydrogenase and results in extreme ‘hangover’ symptoms when consumed with alcohol. It is a specific inhibitor of aldehyde-dehydrogenase (ALDH1). DSF can be used for the treatment of chronic alcoholism by producing an acute sensitivity to alcohol.
DSF may also have antitumor and chemosensitizing activity.
In vitro: Firstly, Disulfiram (DSF) strongly inhibits constitutive and 5-FU-induced NF-kappaB activity in a dose-dependent manner. It inhibits both NF-kappaB nuclear translocation and DNA binding activity. Secondly, DSF significantly enhances the apoptotic effect of 5-FU on DLD-1 and RKO(WT) cell lines. DSF synergistically potentiated the cytotoxicity of 5-FU to both cell lines. It also effectively abolishes 5-FU chemoresistance in a 5-FU resistant cell line H630 (5-FU) in vitro.
Meanwhile, DSF-copper complex potently inhibits the proteasomal activity in cultured breast cancer MDA-MB-231 and MCF10DCIS cells. Besides, DSF (0.1 nM-10 μM; 72 h) + Cu2+ combination enhance the cytotoxicity on ovarian cancer cell lines. They increase intracellular ROS levels triggering apoptosis of ovarian cancer stem cells. DSF, when combined with Cu2+ or Zn2+, can reduce cyclin A expression in melanoma cells. This mixture also decreases cell proliferation at lower concentrations than just using DSF. Furthermore, DSF inhibits gasdermin D (GSDMD) pore formation in liposomes and inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis and IL-1β secretion in human and mouse cells.
In vivo: First of all, DSF significantly inhibits the tumor growth (by 74%), associated with in vivo proteasome inhibition and apoptosis induction in mice bearing MDA-MB-231 tumor xenografts. Besides, DSF blocks the P-glycoprotein extrusion pump, inhibits the transcription factor nuclear factor-kappaB, sensitizes tumors to chemotherapy, reduces angiogenesis, and inhibits tumor growth in mice. Finally, DSF inhibits growth and angiogenesis in melanomas transplanted in severe combined immunodeficient mice.
In addition, Disulfiram is an orally active ALDH1 inhibitor for chronic alcohol dependence and cancer research.
Reference:
[1] Kleczkowska P, et al. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 5;904:174143.
[2] Chen D, et al. Cancer Res. 2006 Nov 1;66(21):10425-33.