Excessive glutamate release, Ca++ overload, free radical generation, poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) overactivation are the main events of neuronal cell death in ischemic stroke. Besides, stroke is a third leading cause of death after heart diseases and cancer and a major cause of disabilities throughout the world. Moreover, excessive generation of peroxynitrite and other free radicals cause massive DNA damage resulting in PARP overactivation. Furthermore, overactivated PARP transforms NAD into long polymers of poly (ADP-ribose) leading to depletion of NAD and subsequently a drastic decrease in cellular ATP pool. Additionally, PARP is important in the regulation of matrix metalloproteinase activity and nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) in cerebral ischemia. Accumulating evidence implicate the role of PARP overactivation in cerebral IR injury. NU1025 is a potent PARP inhibitor with anti-cancer and neuroprotective activity.
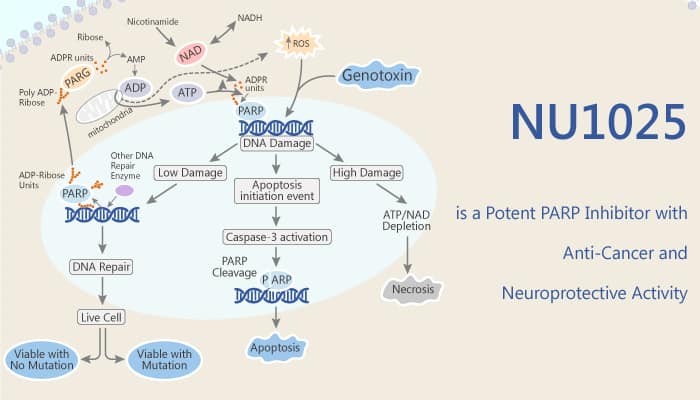
NU1025 is a potent PARP inhibitor with an IC50 of 400 nM and a Ki of 48 nM. Specifically, NU1025 potentiates the cytotoxicity of ionizing radiation and anticancer drugs. In addition, NU1025 has anti-cancer and neuroprotective activity. Pretreatment with NU1025 (0.2 mM) restored cell viability to approximately 73 and 82% in H2O2 and SIN-1 injured cells, respectively. Meanwhile, NU1025 at 1 and 3 mg/kg reduced total infarct volume to 25% and 45%, respectively, when administered 1 h before reperfusion. Nonetheless, NU1025 also produced significant improvement in neurological deficits. Neuroprotection with NU1025 was associated with a reduction in PAR accumulation, a reversal of brain NAD depletion and a reduction in DNA fragmentation. All in all, NU1025 is a potent PARP inhibitor with anti-cancer and neuroprotective activity.
References:
Kaundal RK, et al. J Biol Chem. ife Sci. 2006 Nov 10;79(24):2293-302.