Heat shock protein (Hsp) 90 is a chaperone protein. In addition to protecting cells by correcting misfolded proteins, Hsp90 also plays a key role in regulating the stability, maturation, and activation of a wide range of client substrates, including kinases, hormone receptors, and transcription factors. Most Hsp90 client proteins, such as HER2, Akt, Raf-1, Cdk4, Bcr-Abl, and p53, are essential for cancer cell survival and proliferation. The chaperoning of these client proteins is regulated by a dynamic cycle driven by ATP binding to Hsp90 and subsequent hydrolysis of the protein. Hsp90 requires a series of co-chaperones to form a complex in order to function. These co-chaperones bind to the super-chaperone complex and are released at various time points to regulate the folding, assembly, and maturation of Hsp90 client proteins. In this study, Conglobatin is an orally active Hsp90 inhibitor.
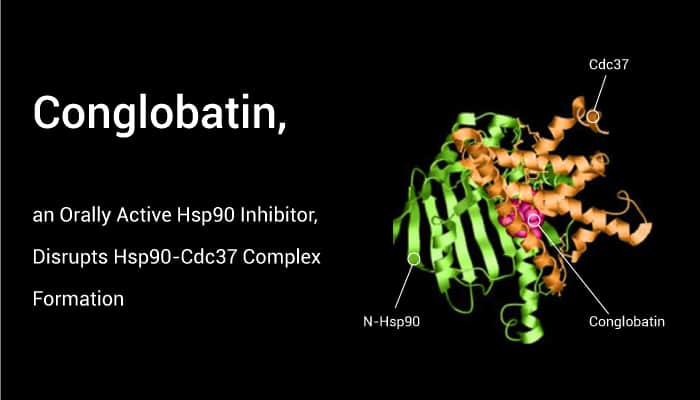
Conglobatin, a potent Hsp90 inhibitor, binds to the N-terminal of Hsp90 and inhibits Hsp90/Cdc37 interaction.
Conglobatin, a macrolide dilactone, is an orally active Hsp90 inhibitor. It can bind to the N-terminal domain of Hsp90 and disrupt Hsp90-Cdc37 complex formation. In addition, Conglobatin induces apoptosis in human breast cancer cells and esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells and exhibits antitumor activity. Conglobatin markedly inhibits the proliferation of SKBR3 and MCF-7 cells, with IC50s of 12.11 and 39.44 μM, respectively. It also displays obvious arrest of SKBR3 and MCF-7 cells in the G2/M phase. It induces apoptosis through caspase-dependent pathways in SKBR3 and MCF-7 cells. Moreover, Conglobatin reduces Hsp90 client protein levels and induces proteasome-dependent degradation. Conglobatin binds to the N-terminal of Hsp90, does not affect ATP-binding capability of Hsp90, but inhibits Hsp90/Cdc37 chaperone/co-chaperone interactions. It also inhibits the tumor growth of SKBR3 and MCF-7 human breast cancer xenograft models in a dose-dependent manner.
In summary, Hsp90 is a promising therapeutic target. inhibition of Hsp90 will presumably result in suppression of multiple signaling pathways. Conglobatin is an orally active Hsp90 inhibitor. It binds to the N-terminal of Hsp90 and inhibits Hsp90/Cdc37 interaction.
Reference:
Huang W, et, al. Mol Cancer. 2014 Jun 14;13:150.