To date, we identified 167 small GTPases in humans which are key signal transducing enzymes. Small GTPases comprise five main families whose eponymous members are Ras, Rho, Rab, ADP-ribosylation factor (Arf) and Ran. Small GTPases link extracellular cues to the neuronal responses required for the construction of neuronal networks, as well as for synaptic function and plasticity. Therefore, different subfamilies of small GTPases play an important in non-neoplastic cerebral diseases, such as Alzheimer’s disease (AD), Parkinson’s disease (PD), intellectual disability, epilepsy, drug addiction, Huntington’s disease (HD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and a large number of idiopathic cerebral diseases.
Ras family proteins are almost universal components of signaling pathways in eukaryotic organisms. The small GTPases from the Ras superfamily play crucial roles in basic cellular processes during practically the entire process of neurodevelopment. Ras family can regulate the cytoplasmic signaling network by binding to a variety of effector molecules with different catalytic activities. Thus, Ras family members can regulate cell proliferation, differentiation, morphology, and apoptosis.
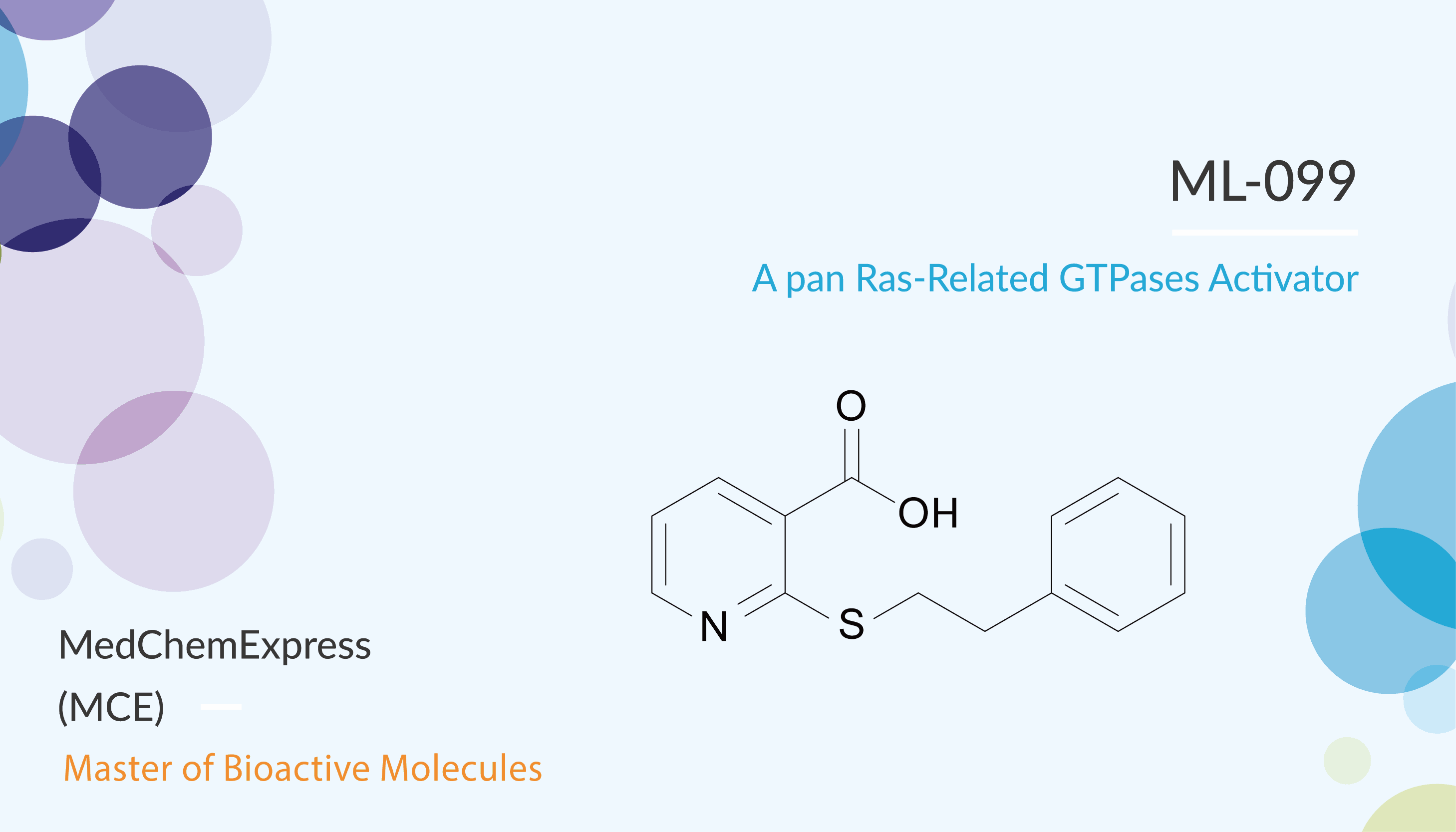
ML-099 is a pan Ras-related GTPases activator. ML-099 can activate Rac1, cell division cycle 42, Ras, Rab7, and Rab-2A. Treatment of resting RBL-2H3 cells with 888706 causes a remarkable transformation in cell surface topography and shape. Strikingly, the addition of the inhibitor 781112 to cells prior to or after addition of 888706 caused cells to sequentially lose their lamellipodia, retract from the substrate, and become progressively more round as they returned to a resting cell morphology within 75 min of inhibitor addition.
All in all, ML-099 is a pan Ras-related GTPases activator. ML-099 can activate Rac1, cell division cycle 42, Ras, Rab7, and Rab-2A.
Reference:
[1]. Qu L, et, al. Front Mol Neurosci. 2019 May 21;12:121.