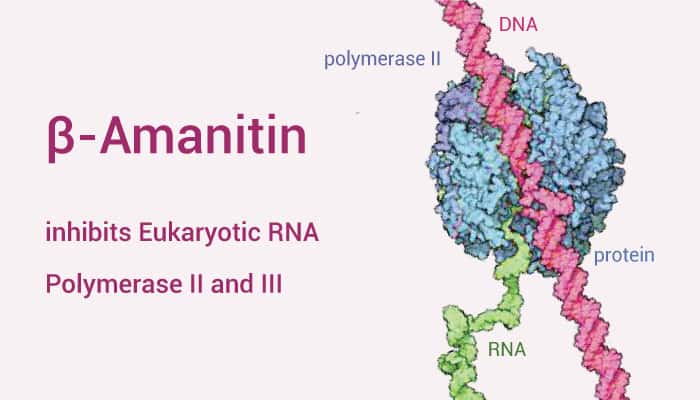
β-Amanitin is a cyclic peptide toxin in the poisonous Amanita phalloides mushroom. Besides, β-Amanitin inhibits eukaryotic RNA polymerase II and III. It inhibits DNA transcription and protein synthesis. Moreover, β-Amanitin can be used as a cytotoxic component of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).
β-Amanitin (0.01-100 µg/mL; 36 hours) shows toxicity in MCF-7 cells, and the rates of cell viability is 52%, 62%, 84%, 86%, and 91% at concentrations of 100, 10, 1, 0.1, and 0.01 µg/mL, respectively. β-Amanitin shows a great inhibition of protein synthesis at both concentrations (10 µg/mL and 1 µg/mL) in MCF-7 cells for 24 hours.
Recently, research has shown the toxicokinetics of β-Amanitin in mice. The results show that β-Amanitin (0.2, 0.4, and 0.8 mg/kg, i.v.) increases the area under plasma concentration curves (AUC). In addition, β-amanitin disappeared rapidly from plasma with a half-life of 18.3–33.6 min, and 52.3% of the iv dose was recovered as a parent form. What’s more, After oral administration of β-Amanitin, the AUC again increases in proportion with doses of 2, 5, and 10 mg/kg. Besides, β-amanitin weakly or negligibly inhibits major cytochrome P450 and 5′-diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase activities in human liver microsomes. Moreover, β-amanitin suppresses drug transport functions in mammalian cells that overexpress transporters.
In conclusion, β-Amanitin is a toxic bicyclic octapeptide present abundantly in Amanitaceae mushrooms. Besides, β-Amanitin inhibits RNA polymerase II and III, DNA transcription, and protein synthesis. Furthermore, β-Amanitin shows toxicity in MCF-7 cells and toxicokinetics in mice.
[1] Kaya E, et al. Turk J Med Sci. 2014;44(5):728-32.
[2] Kaya E, et al. Turk J Med Sci. 2014;44(5):728-32.
[3] Bang YY, et al. Pharmaceutics. 2022 Apr 1;14(4):774.