STING, stimulator of interferon gene, is an important protein in innate immunity. It can induce the production of type I interferon. STING performs an antiviral activity and innate immune response to inhibit intracellular pathogens. ADCs, antibody-drug conjugates, are popular targeted therapies tools for cancer. An ADC consists of a cytotoxic or bioactive payload coupled with an antibody. Specifically, it combines the targeting characteristics of monoclonal antibodies with the cytotoxicity of effective vectors. So it’s a powerful assistant in anticancer research. ADCs release payload cleaved by hydrolytic enzymes or acidic environment in cancer. Then, payload will lead to the apoptosis of cancer cells. Here we’ll introduce a payload, Dazostinag, a STING agonist as well. Nowadays, more and more ADC products try to use non-cytotoxic payloads, such as immunomodulator, as the bullet head of ADC. STING agonist will show extraordinary talents in ADCs research.
Dazostinag serves as a STING agonist as well as a suitable payload of antibody-drug conjugate (ADC).
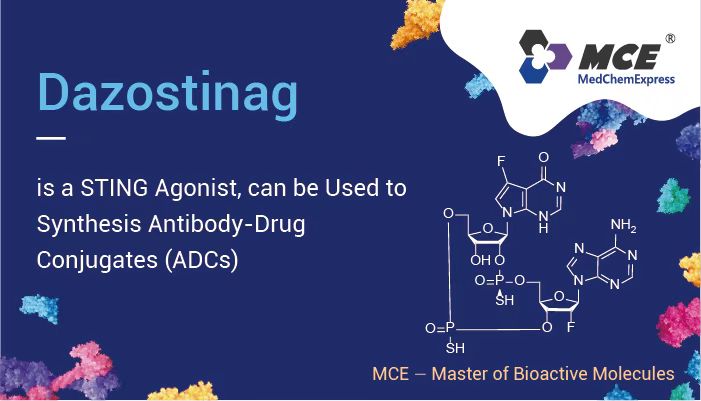
In vitro studies, Dazostinag is an interferon gene stimulant (STING) protein agonist. It (121 μM; 10 min-24 hr) exhibits a half-life (t1/2) of 2.4 hours in rat liver triploid. It (10 μg/mL; 0-96 hr) also shows stability in human, primate, and mouse plasma. It also activates human guanylate cyclase C (GCC) in THP1 cells.
In vivo studies, Dazostinag (0.1 mg/kg; Single dose) has a half-life of 33 h and an AUC (last) value of 51432 h·nM in Balb/C mice with CT26-GCC tumors. It (50 μg/kg, 100 μg/kg; iv; single dose) also significantly inhibits the tumor growth of the CT26 colon cancer model in mice.
In conclusion, Dazostinag is an effective STING agonist with antitumor activity in vivo and in vitro. And it acts as the payload of ADC for the study of malignant tumors.
[1] Ishii Yumiko, et al. World Intellectual Property Organization, WO2020229982. 2020-11-19.
[2] WHO Drug Information-World Health Organization (WHO).