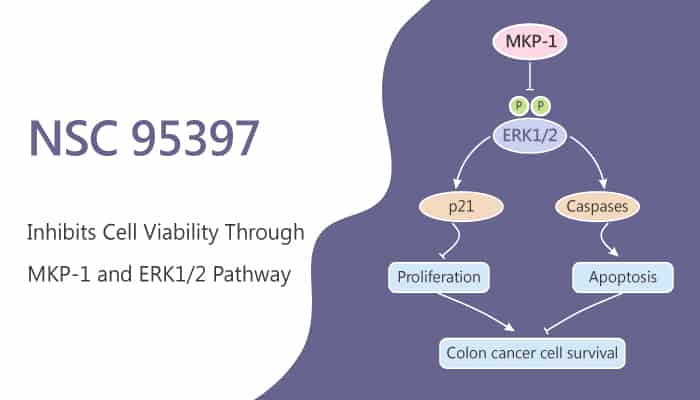
Colon cancer is one of the most common cancers worldwide. Notably, in colon cancer, MKP-1 is overexpressed in the early phases of carcinogenesis. Mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphatase-1 (MKP-1) is a member of dual-specificity phosphatases. MKP-1 inactivates MAPKs by dephosphorylating both their threonine and tyrosine residues.
MAPK pathways play important roles in a broad spectrum of cellular processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, migration and apoptosis. MAPKs are a group of highly conserved protein kinases comprising several subclasses, including ERK1/2, JNKs, and p38 MAPKs. MAPKs mediate both physiological and pathological responses to various extracellular and intracellular stimuli. Researchers have detected overexpression of MKP-1 in several cancers, including breast, lung, prostate, ovarian, pancreatic, and gastric cancer. MKP-1 has promotes angiogenesis and metastasis in lung cancer; but inhibits cell proliferation, metastasis, and angiogenesis in gallbladder cancer. Thus, MKP-1 plays either pro- or anti-tumor role depending on the specific tumor context. Besides, the inhibition of MKP-1 also promotes Gemcitabine sensitivity in pancreatic cancer, Dexamethasone sensitivity in lung cancer, and the sensitivities of three chemotherapy drugs (Mechlorethamine, Doxorubicin, and Paclitaxel) in breast cancer.
NSC 95397 is an inhibitor for dual-specificity phosphatases, including MKP-1. Firstly, NSC 95397 reduces cell viability of colon cancer cells. In addition to anti-proliferation, researchers also find that NSC 95397 induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells. NSC 95397 also induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Besides, NSC 95397 reduces cell proliferation by inhibiting the expression of cell cycle regulatory proteins. Taken together, researchers demonstrate that NSC 95397 is a viable therapeutic intervention for colon cancer via the inhibition of MKP-1 activity.