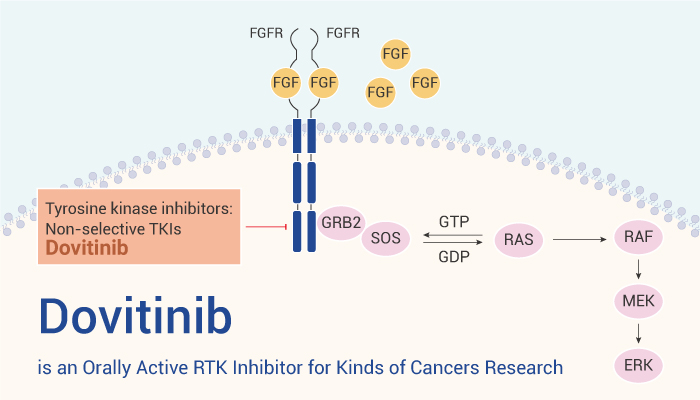
The multi-targeted receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) family includes the receptors for insulin and for many growth factors, such as EGF, FGF, PDGF, VEGF, and NGF. Besides, RTKs are transmembrane glycoproteins that are activated by the binding of their ligands. When binding to the ligands, it transduces the extracellular signal to the cytoplasm by phosphorylating tyrosine residues on the receptors themselves and on downstream proteins. Therefore, RTKs regulates cell proliferation, differentiation, migration, or metabolic changes, and plays an important role in cancers. Importanly, Dovitinib (CHIR-258) is an orally active and potent multi-targeted RTK inhibitor, and has potent antitumor activity in various types of cancer. Moreover, Dovitinib has a safe and effective pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic profile.
Dovitinib, an orally active and multi-targeted RTK inhibitor, can be used for cancer research.
In vitro, Dovitinib inhibits RTKs with IC50s of 1-210 nM for FLT3, c-Kit, CSF-1R, FGFR1/FGFR3, VEGFR1/VEGFR2/VEGFR3, PDGFRα/PDGFRβ, respectively. Besides, Dovitinib (12.5-400 nM; 48 h) potently inhibits the FGF-stimulated growth of WT and F384L-FGFR3-expressing B9 cells with an IC50 of 25 nM. In addition, Dovitinib (100, 500 nM; 96 h) inhibits FGF-mediated ERK1/2 phosphorylation. It also induces apoptosis of FGFR3-expressing human myeloma cells. Apart from antitumor activity, Dovitinib (0-1 μM, 2 days) also enhances BMP-2-induced osteoblast differentiation (marker: ALP induction).
In vivo: Dovitinib (10-60 mg/kg/day; oral; 21 days) shows significant antitumor effect in a xenograft mouse model of FGFR3 multiple myeloma. And the specific tumor growth inhibition rate is 48%, 78.5%, and 94% respectively. Moreover, the Ki-67 staining result demonstrates that CHIR-258 inhibits tumor cell growth and induces apoptosis. In addition, Dovitinib (50, 75 mg/kg) results in 97% and 98% tumor growth inhibition in a hepatocellular carcinoma xenograft mouse model.
In conclusion, Dovitinib, an orally active trosine kinase inhibitor. Dovitinib has antitumor effects and can be used for kinds of cancer research.
References:
[1] Trudel S, et al. Blood. 2005 Apr 1;105(7):2941-8.
[2] Huynh H, et al. J Hepatol. 2012 Mar;56(3):595-601.
[3] Lee Y, et al. Mol Cells. 2016 May 31;39(5):389-94.