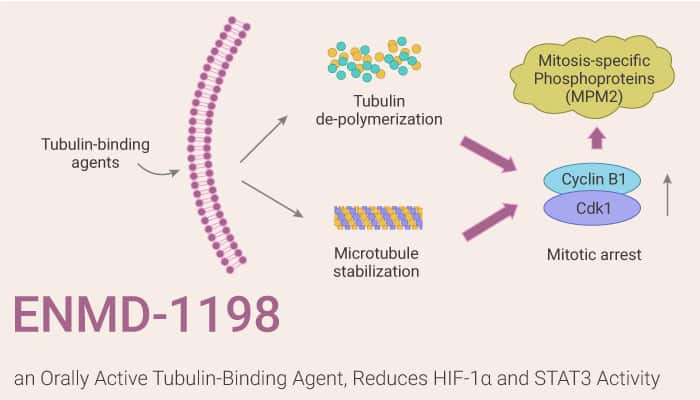
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most cancer worldwide, with a continuously increasing incidence. HCC represents a hyper vascularized tumor and its progression is closely related to angiogenesis. Hepatocellular carcinoma overexpresses the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). The transcription factor HIF-1α also plays a central role in HCC progression and angiogenesis. Furthermore, the transcription factor signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), yet another inducer of angiogenesis in terms of up-regulating VEGF, is constitutively activated in HCC. 2ME2 impairs activation of HIF-1α through destabilization of microtubules, in addition to exhibiting antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic effects. In this study, ENMD-1198, a new analog of 2-methoxyestradiol, displays both antiangiogenic and vascular-disrupting properties. It is an orally active, microtubule disrupting agent that leads to the arrest of cell division and apoptosis in tumor cells. ENMD-1198 also reduces HIF-1alpha and STAT3 activity in human HCC cells. It also inhibits growth and vascularization.
ENMD-1198 dose-dependently elicits significant antiproliferative effects on HCC cells with an IC50 at 2.5 μM in HUH-7 and HepG2 cells. It substantially disrupts EGF signaling in terms of diminishing downstream phosphorylation of the substrates p44/42 MAPK and Akt. Moreover, ENMD-1198 markedly reduces the activation of STAT3, an important transcription factor for regulating VEGF-A in cancer cells. In addition, it significantly inhibits both EGF- and HGF-mediated cancer cell migration and invasiveness. It also effectively inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma through direct effects on the tumor cells, and also through inhibition of angiogenesis. ENMD-1198 -based combination treatments reduce tumor burden but do not eradicate the tumor in mice. ENMD-1198 treatment protects the bone against tumor-induced osteolysis in vivo.
In summary, ENMD-1198 is an analog of 2ME2 with antiproliferative and antiangiogenic activity. Moreover, it effectively diminishes both HIF-1α and STAT3 activation in HCC cells, which represent important mediators of HCC progression.
Reference:
Moser C, et al. BMC Cancer. 2008 Jul 23;8:206.